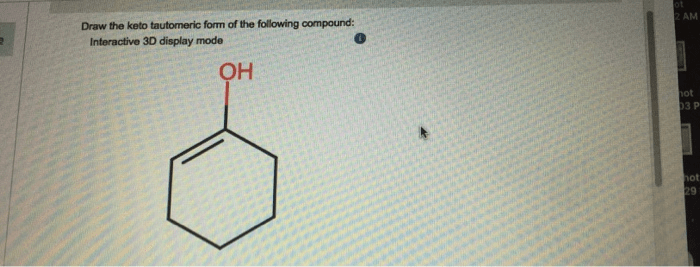
Delving into the realm of keto-enol tautomerism, we embark on an exploration of the structural transformations that define this fascinating chemical phenomenon. Draw the keto tautomeric form of the following compound, an intriguing proposition that unveils the intricacies of this dynamic process.
As we delve deeper into the world of keto tautomers, we uncover their unique structural features and witness the interplay of factors that govern their equilibrium. From the influence of pH to the role of temperature and solvent effects, we unravel the secrets behind these molecular shape-shifters.
Keto Tautomeric Form
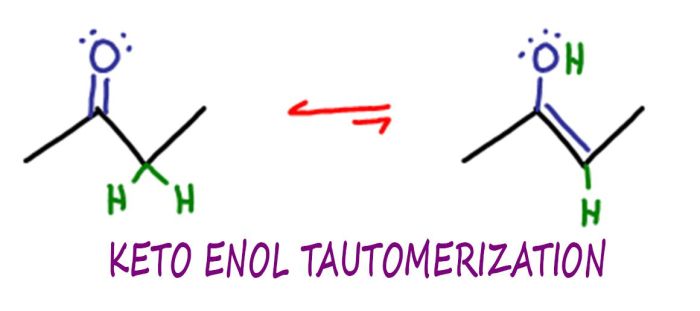
Keto-enol tautomerism is a reversible isomerization reaction that involves the interconversion of a keto group (C=O) and an enol group (C=C-OH). This isomerization occurs through a proton transfer reaction, where a proton is transferred from the α-carbon of the keto group to the oxygen atom of the keto group, resulting in the formation of the enol tautomer.
Structural Features of a Keto Tautomer
- Contains a carbonyl group (C=O) double bond.
- Has an α-carbon (the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group) with a hydrogen atom.
- The α-carbon and the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group are in a trans configuration.
Examples of Keto Tautomers
- Acetaldehyde (keto form: CH3CHO; enol form: CH2=CHOH)
- Acetone (keto form: CH3COCH3; enol form: CH2=C(OH)CH3)
- 2-Butanone (keto form: CH3CH2COCH3; enol form: CH3CH=C(OH)CH3)
Drawing Keto Tautomeric Forms
To draw the keto tautomeric form of a compound, follow these steps:
- Identify the keto group in the compound.
- Move a proton from the α-carbon to the oxygen atom of the keto group.
- Redraw the double bond to form a carbon-carbon double bond and a hydroxyl group (-OH).
Example: Drawing the Keto Tautomer of Acetaldehyde
- Keto form: CH3CHO
- Move the proton from the α-carbon to the oxygen atom:
- Redraw the double bond:
- Keto tautomer: CH2=CHOH
| Property | Keto Form | Enol Form |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Group | Carbonyl group (C=O) | Carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and hydroxyl group (-OH) |
| Carbonyl Carbon | sp2 hybridized | sp2 hybridized |
| α-Carbon | sp3 hybridized | sp2 hybridized |
| Polarity | Polar | Less polar |
| Reactivity | More reactive | Less reactive |
Factors Affecting Tautomerization
The equilibrium between keto and enol tautomers is influenced by several factors:
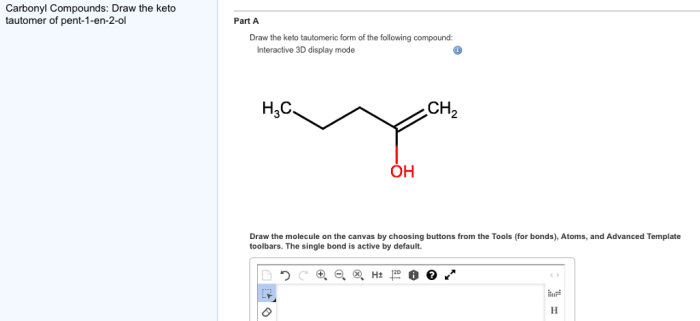
pH, Draw the keto tautomeric form of the following compound
In acidic solutions, the keto form is favored, while in basic solutions, the enol form is favored. This is because the protonation of the enol form in acidic solutions shifts the equilibrium towards the keto form.
Temperature
Increasing temperature favors the enol form. This is because the enol form is more stable at higher temperatures due to its higher entropy.
Solvent
The polarity of the solvent can affect the equilibrium. Polar solvents favor the keto form, while nonpolar solvents favor the enol form.
Examples
- In acidic solutions, acetone exists predominantly as the keto form (99%).
- In basic solutions, acetone exists predominantly as the enol form (99%).
- In nonpolar solvents, acetone exists as a mixture of keto and enol forms (approximately 50:50).
Applications of Keto-Enol Tautomerism
Keto-enol tautomerism plays a significant role in organic chemistry, affecting the reactivity and properties of compounds:
- Enolates as Nucleophiles:Enolates, which are formed from the deprotonation of enols, are strong nucleophiles that can undergo various reactions, such as alkylation, acylation, and aldol condensation.
- Keto-Enol Tautomerization in Biological Systems:Keto-enol tautomerism is essential for the function of many enzymes, such as ketosteroid isomerase and pyruvate kinase, which catalyze reactions involving the interconversion of keto and enol forms.
- Tautomerism in Drug Design:The ability of compounds to undergo keto-enol tautomerism can influence their biological activity and pharmacokinetic properties.
FAQ Compilation: Draw The Keto Tautomeric Form Of The Following Compound
What is the significance of keto-enol tautomerism?
Keto-enol tautomerism plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes, including enzyme catalysis, acid-base reactions, and the reactivity of carbonyl compounds.
How can we predict the equilibrium position of keto-enol tautomers?
The equilibrium position of keto-enol tautomers is influenced by several factors, including the acidity of the medium, the nature of the substituents on the carbon-carbon double bond, and the solvent effects.