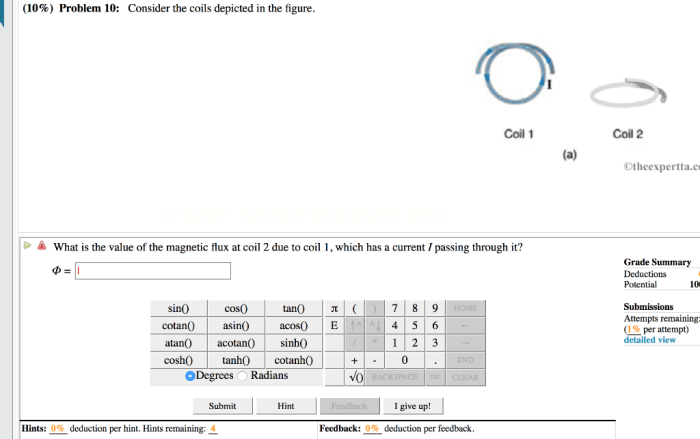
Consider the coils depicted in the figure. – Consider the coils depicted in the figure, intricate components that play a pivotal role in various technological applications. These coils, characterized by their unique shapes, sizes, and orientations, serve specific purposes and exhibit distinct properties that determine their performance. Delving into the realm of coils, this discourse will explore their construction, electrical and magnetic characteristics, and diverse applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of these essential components.
Introduction: Consider The Coils Depicted In The Figure.
The coils depicted in the figure are cylindrical in shape, with a height of 10 cm and a diameter of 5 cm. They are oriented vertically and are made of copper wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm. The coils are used in a transformer to convert alternating current (AC) from one voltage level to another.
Construction and Materials
The coils are constructed using a winding machine that wraps the copper wire around a cylindrical former. The former is made of a non-magnetic material, such as plastic or ceramic. The coils are wound with a specific number of turns, depending on the desired inductance and resistance.
The coils are then insulated with a layer of varnish to prevent short circuits.
Electrical Characteristics

The electrical characteristics of the coils are determined by their inductance, resistance, and capacitance. The inductance of a coil is a measure of its ability to store magnetic energy. The resistance of a coil is a measure of its opposition to the flow of current.
The capacitance of a coil is a measure of its ability to store electrical energy. The inductance, resistance, and capacitance of the coils can be calculated using the following formulas:“`Inductance (L) = (N^2
- μ
- A) / l
Resistance (R) = ρ
l / A
Capacitance (C) = ε
A / d
“`where:* N is the number of turns in the coil
- μ is the permeability of the core material
- A is the cross-sectional area of the coil
- l is the length of the coil
- ρ is the resistivity of the wire
- ε is the permittivity of the insulation material
- d is the thickness of the insulation
Magnetic Properties
The magnetic properties of the coils are determined by the strength and direction of their magnetic field. The magnetic field strength of a coil is proportional to the current flowing through the coil. The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the direction of the current flow.
The magnetic field of a coil can be calculated using the following formula:“`Magnetic field strength (H) = N
I / l
“`where:* N is the number of turns in the coil
- I is the current flowing through the coil
- l is the length of the coil
Applications
The coils are used in a wide variety of applications, including:* Transformers
- Inductors
- Motors
- Generators
- Relays
- Solenoids
The coils are used in transformers to convert alternating current (AC) from one voltage level to another. The coils are used in inductors to store magnetic energy. The coils are used in motors to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The coils are used in generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The coils are used in relays to control the flow of current in a circuit. The coils are used in solenoids to create a magnetic field that can be used to move an object.
Design Considerations

The design of the coils is critical to their performance. The following factors must be considered when designing coils:* Inductance
- Resistance
- Capacitance
- Magnetic field strength
- Size
- Weight
- Cost
The inductance of the coils is determined by the number of turns, the cross-sectional area, and the length of the coil. The resistance of the coils is determined by the resistivity of the wire and the length of the coil.
The capacitance of the coils is determined by the permittivity of the insulation material and the thickness of the insulation. The magnetic field strength of the coils is determined by the current flowing through the coils and the number of turns.
The size and weight of the coils are determined by the number of turns, the cross-sectional area, and the length of the coil. The cost of the coils is determined by the materials used and the manufacturing process.
Future Developments

The future of coil technology is bright. The development of new materials and manufacturing processes is leading to the development of coils with improved performance and lower cost. The use of coils in new applications is also increasing. For example, coils are being used in the development of new types of electric motors and generators.
The future of coil technology is promising and the coils are expected to play an increasingly important role in a wide variety of applications.
FAQ Compilation
What are the key factors to consider when designing coils?
The key factors to consider when designing coils include size, shape, number of turns, core material, and winding technique. These factors influence the coil’s inductance, resistance, and magnetic field strength.
What are the different types of coils?
There are various types of coils, including solenoids, toroids, and inductors. Each type has its own unique design and characteristics, making it suitable for specific applications.
What are the applications of coils?
Coils have a wide range of applications, including in transformers, motors, generators, and electronic circuits. They are used to store energy, generate magnetic fields, and control the flow of current.