Mr friedhoff mendelian genetics packet – Mr. Friedhoff’s Mendelian Genetics Packet serves as a comprehensive guide to the foundational principles of genetics, providing an in-depth examination of the contributions of Gregor Mendel and the significance of his experiments with pea plants. This packet offers a detailed timeline of key events in the development of Mendelian genetics, ensuring a thorough understanding of its historical context.
The packet delves into the core concepts of Mendelian inheritance, including dominance, recessiveness, and segregation. It explores the concept of genetic alleles and genotypes, elucidating the different types of inheritance patterns, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and sex-linked. This comprehensive resource provides a solid foundation for understanding the applications of Mendelian genetics in various fields, including agriculture, medicine, and forensic science.
1. Historical Context of Mendelian Genetics
Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian monk and scientist, is widely recognized as the father of modern genetics. His groundbreaking experiments with pea plants, conducted in the mid-1800s, laid the foundation for our understanding of inheritance patterns.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1856: Mendel begins his experiments with pea plants.
- 1865: Mendel presents his findings to the Brünn Natural History Society.
- 1866: Mendel’s paper on inheritance is published.
- 1900: Mendel’s laws are rediscovered by Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erich Tschermak.
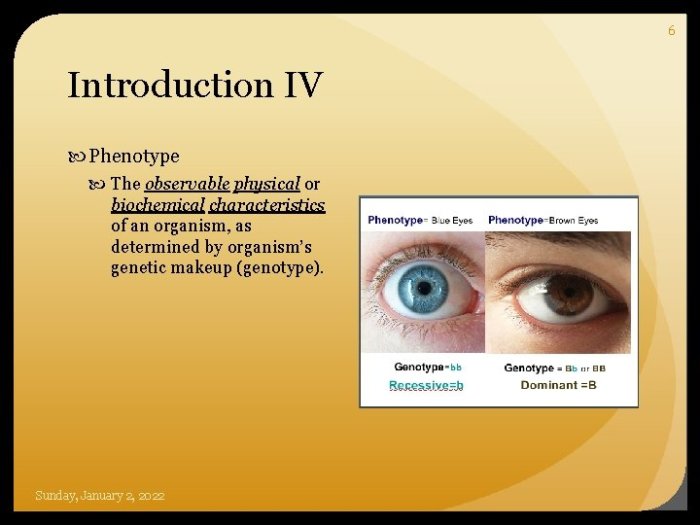
2. Key Concepts of Mendelian Genetics: Mr Friedhoff Mendelian Genetics Packet
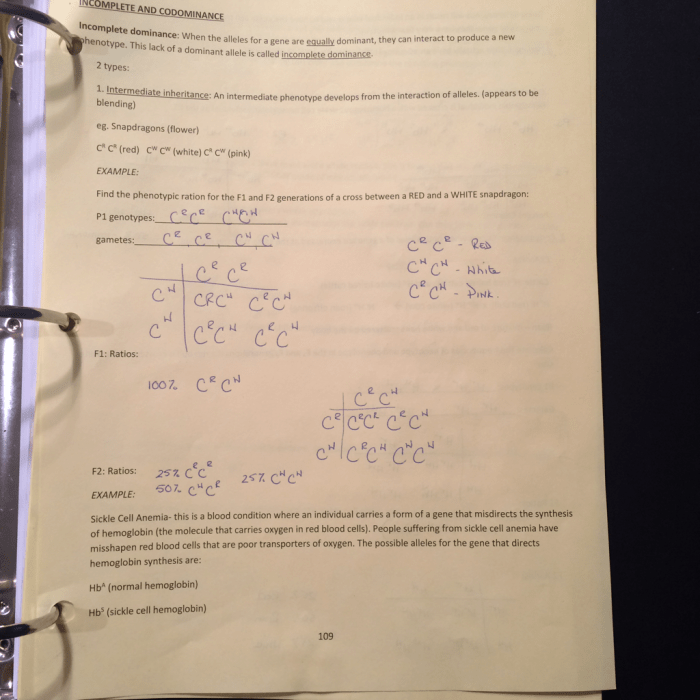
Mendel’s experiments revealed several fundamental principles of inheritance, known as Mendelian genetics. These principles include:
Dominance and Recessiveness
In a pair of alleles, the dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele. The dominant allele is expressed in both homozygous and heterozygous individuals, while the recessive allele is only expressed in homozygous individuals.
Segregation, Mr friedhoff mendelian genetics packet
During meiosis, the two alleles of a gene separate and segregate into different gametes (eggs or sperm). This ensures that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
3. Applications of Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics has numerous practical applications in various fields:
Agriculture
Mendelian principles are used to breed plants and animals with desired traits, improving crop yields and livestock production.
Medicine
Mendelian genetics helps identify genetic disorders, predict inheritance patterns, and develop targeted therapies.
Forensic Science
DNA analysis based on Mendelian principles is used in criminal investigations to identify individuals and establish relationships.
4. Extensions and Refinements of Mendelian Genetics

While Mendelian genetics provides a solid foundation for understanding inheritance, it has been extended and refined over time:
Non-Mendelian Inheritance Patterns
Some inheritance patterns deviate from Mendelian principles, such as incomplete dominance, codominance, and polygenic inheritance.
Molecular Genetics
Molecular genetics has provided a deeper understanding of the molecular basis of inheritance, including the role of DNA and genes.
FAQ Section
What are the key principles of Mendelian inheritance?
The key principles of Mendelian inheritance include dominance, recessiveness, and segregation. Dominance refers to the expression of one allele over another, while recessiveness refers to the masking of an allele by a dominant allele. Segregation refers to the separation of alleles during gamete formation.
What are the different types of inheritance patterns?
The different types of inheritance patterns include autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and sex-linked. Autosomal dominant inheritance refers to traits that are expressed when a dominant allele is present on either chromosome of a homologous pair. Autosomal recessive inheritance refers to traits that are only expressed when a recessive allele is present on both chromosomes of a homologous pair.
Sex-linked inheritance refers to traits that are located on the X or Y chromosome.