Should we terraform mars answer key – Should we terraform Mars? This question has captivated the minds of scientists, engineers, and science fiction enthusiasts for decades. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the multifaceted implications of terraforming Mars, exploring the potential environmental impacts, technological challenges, economic viability, ethical considerations, scientific value, and public perception surrounding this ambitious endeavor.
As we embark on this journey, we will examine the potential benefits and risks of terraforming Mars, weighing the scientific advancements against the ethical responsibilities and economic uncertainties that accompany such a transformative undertaking.
Environmental Impact

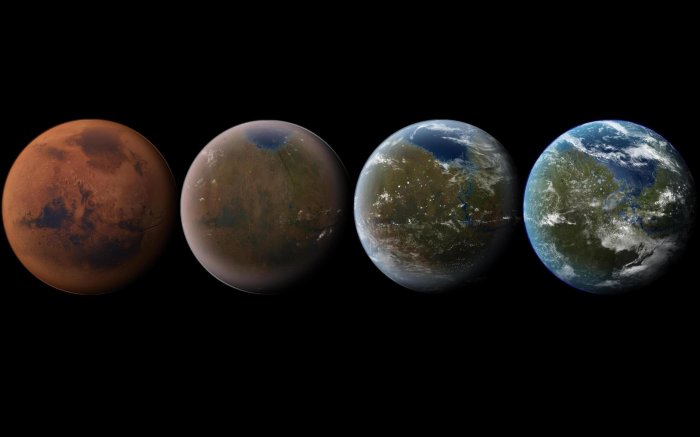
Terraforming Mars, the process of altering the planet’s atmosphere and surface to make it habitable for humans, has the potential to significantly impact its environment.
The release of greenhouse gases during terraforming could contribute to global warming on Mars, potentially leading to changes in the planet’s climate and the melting of its polar ice caps. This could result in the loss of water resources and the disruption of ecosystems.
Additionally, the introduction of new organisms to Mars as part of the terraforming process could have unforeseen consequences for the planet’s natural ecosystems. The potential for unintended species interactions and competition for resources raises ethical concerns about the disruption of Mars’s pristine environment.
Technological Feasibility
Current technological capabilities for terraforming Mars are limited, and the process would require significant advancements and innovations.
One major challenge is the need to create a breathable atmosphere on Mars. This would involve generating oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the planet’s atmosphere, a complex and energy-intensive process.
Another challenge is the need to warm Mars’s surface temperature. This could be achieved through the use of greenhouse gases or the introduction of reflective materials to increase solar radiation absorption. However, the long-term stability and effectiveness of these methods are still uncertain.
Economic Viability
Terraforming Mars would require substantial financial investments, both in the initial stages and for the long-term maintenance of a Martian colony.
The costs of terraforming include the development and deployment of advanced technologies, the transportation of materials and equipment to Mars, and the establishment of a sustainable infrastructure on the planet.
The potential economic benefits of terraforming Mars are uncertain and depend on the success of the terraforming process and the ability to establish a thriving colony on the planet.
Ethical Considerations

Terraforming Mars raises ethical concerns related to the potential impact on any existing life forms on the planet.
The introduction of Earth-based organisms to Mars could have unintended consequences for the planet’s native ecosystems. It is important to consider the potential for disrupting or even destroying indigenous life on Mars, and to take appropriate measures to mitigate these risks.
Additionally, the decision to terraform Mars involves ethical considerations related to the allocation of resources and the prioritization of human interests over the preservation of the planet’s natural environment.
Scientific Value
Terraforming Mars would provide a unique opportunity for scientific research and exploration.
The process of terraforming would allow scientists to study the effects of atmospheric and surface modifications on a planetary scale, providing valuable insights into the processes that shape planetary environments.
Additionally, a terraformed Mars could serve as a base for further exploration of the solar system, providing a platform for missions to other planets and moons.
Public Perception and Support: Should We Terraform Mars Answer Key
Public perception of terraforming Mars is influenced by a variety of factors, including environmental concerns, economic implications, and ethical considerations.
Some members of the public support terraforming as a way to expand human presence in space and to potentially create a new home for humanity. Others are concerned about the environmental risks and the potential for unintended consequences.
Engaging the public and building support for terraforming Mars requires transparent and inclusive communication about the potential benefits and risks, as well as the ethical implications of such a project.
FAQ Overview
What are the potential environmental risks of terraforming Mars?
Terraforming Mars could potentially release greenhouse gases, disrupt the planet’s natural ecosystems, and alter its atmosphere, potentially leading to unintended consequences.
What are the technological challenges of terraforming Mars?
Terraforming Mars requires significant advancements in technology, including methods for altering the atmosphere, warming the planet, and creating a sustainable biosphere.
Is terraforming Mars economically viable?
The economic viability of terraforming Mars is uncertain, with estimates of the costs varying widely. The potential return on investment and the long-term sustainability of a Martian colony are also key considerations.
What are the ethical implications of terraforming Mars?
Terraforming Mars raises ethical questions about the potential impact on any existing life forms on the planet and the responsibilities of humans to respect and preserve the natural environment of other celestial bodies.
What is the scientific value of terraforming Mars?
Terraforming Mars could provide valuable scientific insights into planetary science, the origins and evolution of life, and the potential for human habitation beyond Earth.